Definitions of ESG and CSR to understand the differences and complementarity between these two approaches
ESG or CSR? Learn to differentiate them and better integrate them into your practices.

ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) is a framework for evaluating companies' sustainable practices. While this framework was popularized by Socially Responsible Investment (SRI), it is not limited to investors. Today, ESG is also used by companies themselves, regulators, and all stakeholders to drive their sustainable strategy. On the other hand, CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) refers to a company's voluntary effort to integrate environmental and social issues into its strategy. Thus, while these two approaches are complementary, ESG is based on standardized and measurable criteria, whereas CSR adopts a more global and flexible approach, often initiated by the company itself.
What is ESG: Environmental, Social, and Governance
Definition
ESG is the acronym for Environmental, Social, and Governance issues. These are tools for evaluating the overall performance of companies based on sustainability criteria. These criteria are the pillars of extra-financial analysis.
ESG became prominent from the 2000s with its integration into investors' financial criteria. It evaluates the impact of companies' practices on certain extra-financial criteria.
Indeed, if we break down the different aspects of ESG, we find:
- The environmental pillar, which evaluates the impact of a company on its environment. The company is assessed both on the management of its impact and its ability to mitigate environmental risks.
This criterion takes into account various factors: waste management, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, conservation of natural resources, prevention of environmental risks, etc.
- The social pillar, which evaluates the company's responsibility towards its stakeholders (employees, customers, and communities). This aspect considers: labor rights, supply chain, accident prevention, as well as inclusion and diversity policies.
- The governance aspect, which focuses on how the company is managed. It checks: management structure, board independence, and transparency, among others.
Thus, investors take these three aspects into account when making decisions about responsible investment. In a purely financial approach, some risks and opportunities may not be visible and could distort an organization's value.
The ESG application framework
The ESG application framework is quite broad. It is used by regulators to establish regulatory frameworks and audit ESG practices. It applies to investors, certain listed and unlisted companies, and financial institutions. The ESG framework is based on ESG standards and regulations that harmonize practices and ensure transparency of non-financial information. Among the most important standards is the CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) in Europe, which strengthens corporate reporting requirements on their environmental, social, and governance impacts. This directive requires large companies to publish detailed data on their ESG policies, objectives, and outcomes. For investment funds, the SFDR (Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation) governs the transparency of financial products. These standards ensure a structured framework for assessing sustainable opportunities and impacts, while encouraging companies to adopt more responsible practices.
What is CSR: Corporate Social Responsibility
Definition
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is defined by the European Commission as "the responsibility of enterprises for their impacts on society". This responsibility can be understood as the voluntary integration of environmental and social concerns into business activities. This concerns their internal activities as well as their relationships with stakeholders. It aims to respect the principles of sustainable development and is based on the idea that companies should not only focus on profit, but also positively contribute to society and the planet.
The CSR application framework
However, be aware that even if CSR has developed as a voluntary approach, a legislative and regulatory framework has been organized in France over the past few years, particularly on environmental issues. The most striking example is the adoption of the PACTE law in 2019.
The PACTE law created the status of "société à mission" illustrating the growing importance of CSR for businesses and communities.
Thus, all businesses can undertake a CSR approach regardless of size, sector, or legal form. Undertaking a CSR approach, in addition to meeting regulatory requirements, allows you to:
- Meet consumer and talent expectations
- Reduce risks and costs related to negative impacts
- Improve your image and reputation
What are the differences between ESG and CSR?
Although related to sustainable development, these two concepts have different approaches and objectives.
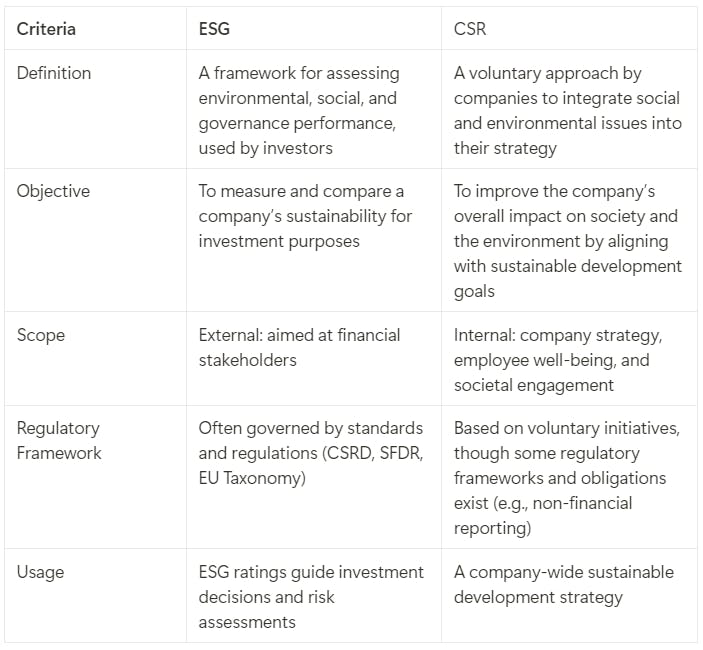
ESG is a standardized framework focused on measurable performance and investment support, while CSR is a voluntary, broader, and more internal approach. CSR is a strategy that the company implements autonomously, independently of its ESG obligations. Thus, a company can have a strong CSR involvement without necessarily achieving satisfactory ESG performance.
The two concepts overlap but do not serve the same objectives.
To clarify, here are some examples.
- A publicly traded company is evaluated by agencies like MSCI or Sustainalytics on its greenhouse gas emissions, board diversity, and anti-corruption policies. These scores influence investor decisions through its ESG score. Thus, Hermès, the French luxury group, has exemplary ESG management, ranking third in the top 100 ESG companies according to ESG Book.
- On the other hand, an SME adopts an ethical charter, reduces plastic waste, promotes remote work, and supports local associations. These initiatives are not measured by financial indicators but strengthen its societal commitment. Its CSR initiatives do not necessarily translate to a good ESG score. Thus, it is important for a company to integrate an ESG strategy if it wants to be well-rated on these aspects.
Why are ESG and CSR complementary?
As we have just seen, these two concepts are linked and therefore complementary:
- CSR feeds ESG: The CSR initiatives implemented by a company form the basis of ESG evaluations. For example, a company that reduces its CO₂ emissions or adopts ethical governance practices directly feeds into ESG indicators. CSR provides the qualitative and quantitative content for investors to evaluate the ESG performance of the company.
- ESG provides a framework and legitimacy to CSR. Indeed, ESG offers a standardized structure that allows measuring and comparing the performance of companies. This framework brings legitimacy to CSR initiatives because it makes them quantifiable and transparent. For instance, the ISO 26000 standard provides guidelines for social responsibility, helping companies structure their CSR actions in a coherent and recognized manner.
- ESG also justifies the financial impact of CSR. CSR criteria translate CSR initiatives into financial indicators. For example, a company that invests in energy efficiency may see a reduction in its operational costs, thus improving its profitability. Similarly, strong governance can reduce the risks of financial scandals, thereby protecting shareholder value. Thus, ESG acts as a bridge between CSR initiatives and the expectations of financial markets, demonstrating that sustainability and responsibility can align with economic performance.
Examples of complementarity between ESG and CSR

Thus, integrating CSR and ESG in the company means combining positive impact with economic performance. It is about evaluating its commitment and boosting its attractiveness to financial stakeholders. To develop these aspects, there are numerous solutions, including ESG software.
Greenscope, with its platform and ESG expertise, offers comprehensive support to help financial players, including investors and large companies, measure their non-financial performance. Contact us to learn more about our support.
Our latest articles

Responsible Digital: the next step after your Carbon Footprint assessment
Understand the importance of implementing a responsible digital approach after completing your carbon footprint assessment

CSR News - April 2025
Discover the key developments: ongoing projects, standards updates, new official documents.

ESG Data: How to identify, collect, and use them
Learn how to structure your ESG data to better drive your commitments and enhance your sustainable performance

Guide on ESG performance: definition, measurement, and impact on business
ESG performance, a driving force for responsible growth: follow our guide to understand everything in just a few minutes



