CSR Strategy: Awareness Programs to Mobilize and Train Teams (ADEME study)
Focus on awareness, with a comprehensive overview of employee mobilization mechanisms in companies.

At Greenscope, we are convinced that regulatory obligations such as CSRD or SFDR represent real opportunities for transformation for organizations. To succeed, it is essential to mobilize all teams, and there are many ways to achieve this. Focus on awareness, with a comprehensive overview of employee mobilization devices in companies.
Introduction
Without a doubt, awareness is a necessary, although not sufficient, means to engage all teams in your CSR approach by involving them in its implementation. Many stakeholders have already understood this, as evidenced by the proliferation of Climate Frescos in recent years: over 1.8 million "fresquées" counted in 2024.
However, it is possible to go further, as shown by the #ECOTAF study by ADEME and sociologist Gaëtan Brisepierre (2023). It highlights the emergence of "ecoworkers," a new category of engaged and change-driving employees. Nevertheless, the transformation of companies requires the commitment of all teams. It is therefore crucial to deploy inclusive mobilization and training programs. Their objective is to harmonize the level of awareness, involve all employees in organizational transformations, and strengthen the coherence of the company's commitment. What are these options, how to select them, and what transformations can they generate?
This article summarizes the conclusions of the #ECOTAF study (ADEME, College of Sustainable Development Directors, Companies for the Environment, Observatory of Corporate Social Responsibility, Action for Market Transformation), conducted by sociologist Gaëtan Brisepierre and his team, published in November 2023. See the complete study for more information.
4 Mobilization Types for 4 Strategies to Encourage Action: Overview of Levers
Focus on the #ECOTAF study aimed at describing the levers that support employees' ecological engagement within the framework of their work, to better understand their articulation with the company's approaches and their effects on employees and the company.
The study categorizes the levers into four categories, which operate on different dynamics for encouraging action.
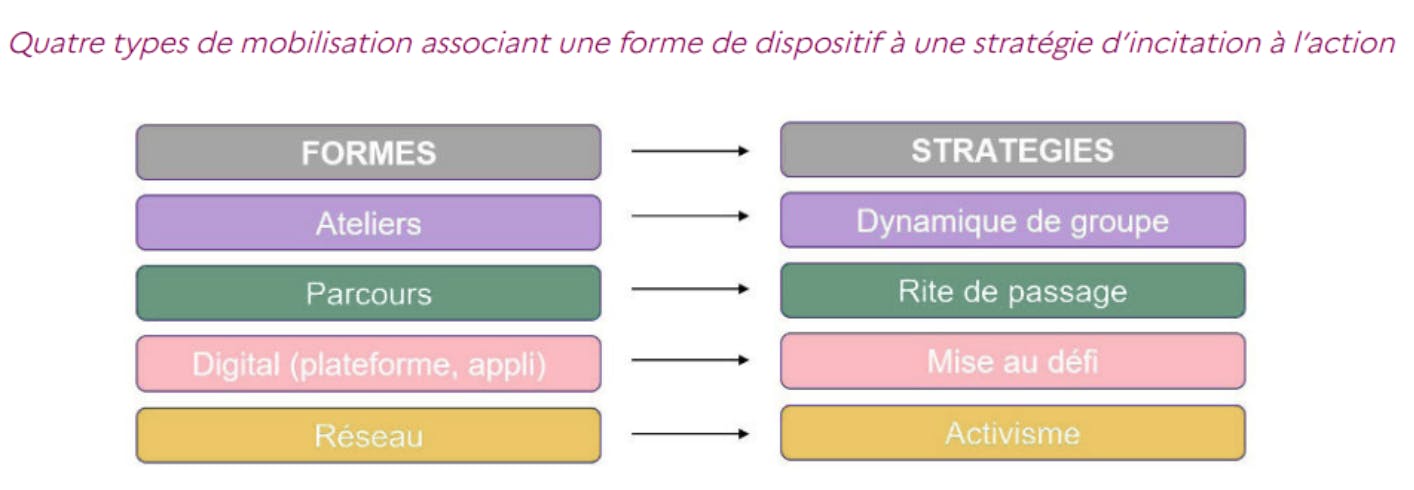
⏩Workshops
Workshops are relatively short meeting times, often in small groups, usually facilitated by an internal or external facilitator to the company. They tap into the dynamic of the peer group: through the sharing of experiences and collective emulation, they create a common culture on ecological issues and legitimize taking action, most often on an individual level.
⇒ EX: 2ton workshops or Our Low Carbon Lives, Climate Fresco (and all existing frescos)…
⏩Courses
The "paths" refer to a different timeline: often over several months, they aim to train employees and support their skill development on CSR issues, or even to accompany them in developing an impact project. They act as a rite of passage for employees who choose to engage in them.
⇒ EX: Corporate for Change
⏩Digital platforms
Digital platforms fit with a timeline similar to paths but rely more on the gamification of employee engagement. Employees are challenged or even put in competition and encouraged to implement CSR actions at their scale, service level, or site level. The experience is more collective and must be guided by "ambassador" employees to work well.
⇒ EX: Lakaa, Ma Petite Planète
⏩Networks
Finally, networks go beyond company boundaries and bring together groups of "activist" employees by creating inter-company exchange spaces. Their action is more political (influence actions), and some are notably trade union organizations.
⇒ EX: Les Collectifs, Réseau FEVE
The study thus classifies 12 programs according to these 4 categories, based on their target and objective:
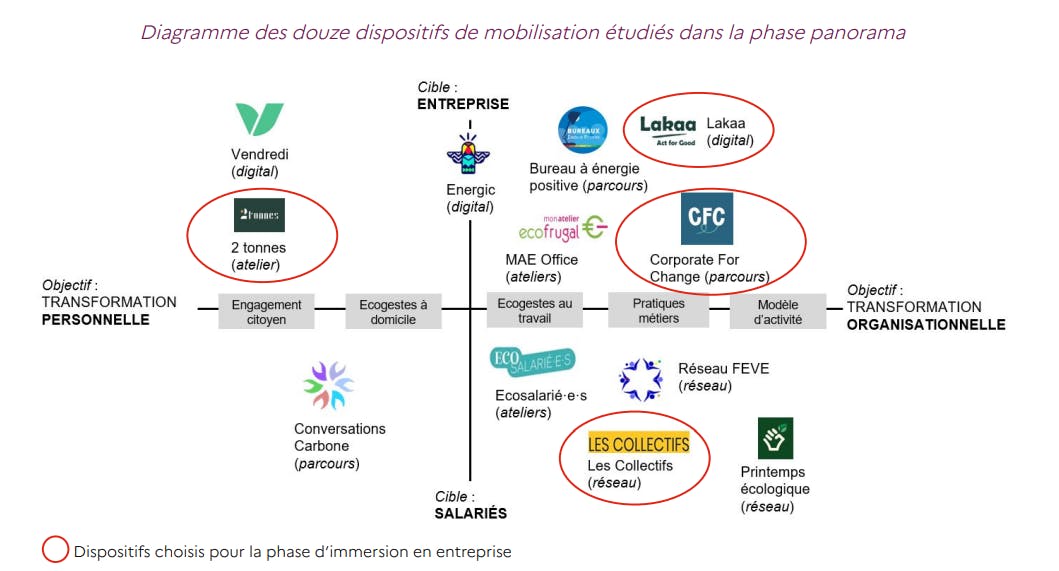
For more information on the studied levers and to choose the one that meets your needs, see the interim study report #ECOTAF which contains very complete analysis sheets of each category.
💡To remember:
- The objectives of the studied devices vary between organizational transformation and personal transformation of employees.
- They may require a one-time investment - workshops - or longer-term - paths, digital platforms, and networks -, whether in time for participants or financial cost for the company.
- The different profiles of employees - little aware or "ecotafeurs" - do not necessarily request the same devices. Some can even initiate the implementation of devices such as networks or challenges and play an ambassador role during their deployment.
To go further: application of training and awareness levers in the company, our advice for effective mobilization
⏩Identify profiles that drive ecological mobilization opportunities
Identifying profiles driving mobilization opportunities is crucial for effectively engaging your teams in the deployment of your CSR strategy and ensuring its consistency:
- Committed employees (or "ecoworkers"): These employees are often the originators of initiatives such as workshops or frescos and are sometimes the facilitators. Identifying these engaged profiles will allow you to involve them in structuring and leading a sensitization policy throughout your company.
- CSR Managers: True pillars of mobilization, they play a key role in integrating initiatives into the company's overall CSR strategy. Their involvement is therefore essential to ensure the sustainability and relevance of initiatives.
⏩Providing means for these employees to engage: time, responsibilities, and budget
The barriers to internal engagement vary according to profiles: lack of time, budget, or projects outside the scope of the employees' missions. To strengthen your CSR policy and mobilize your teams, it is crucial to gradually remove these obstacles:
- For engaged employees: Many report a lack of dedicated time for their ecological engagement within the company. The study highlights certain initiatives aimed at freeing up this time, such as hiring a trainee, the manager signing an engagement mission sheet, or allocating specific time through the company's foundation. A promising idea is the establishment of an “ecological time credit” to support these driving employees.
- For CSR managers: in a context of evolving regulatory frameworks (notably with the CSRD), some CSR managers report being preoccupied with anticipating these new non-financial reporting standards, to the detriment of ecological mobilization initiatives. By unlocking a budget allocated to an ESG reporting solution like Greenscope, you free up time for your CSR team, allowing them to devote more efforts to internal mobilization.
Mobilization initiatives are essential to achieve CSR objectives. They facilitate employees' acclimatization to ecological issues, promote teams' appropriation of the CSR strategy, and allow for the upward flow of transformation proposals from trades to management. It is therefore essential to unlock the necessary resources so that employees can support and participate in them.
⏩Succeed in mobilizing by choosing the right initiative
The success conditions of mobilization in a company depend on many factors: size, culture, and demographics of the company. Furthermore, while the success of an initiative is often measured by the number of participants, other characteristics must also be considered, such as the geographic scope of deployment and the audience reached.
The choice and dissemination of such an initiative must thus be considered according to the expected results: massive awareness of employees? Intensification of the engagement of certain employees? Support for the implementation of concrete projects, in terms of intrapreneurship?
⏩Training teams and involving leaders, to sustainably transform the company
The awareness initiatives mentioned earlier must be reinforced by adapted training plans, to meet the growing needs of teams in terms of transforming trades. These trainings help to durably anchor practices and provide employees with the necessary skills to integrate ecological issues into their missions.
Moreover, the involvement of leaders is crucial to ensure the consistency and effectiveness of mobilization efforts. Besides their participation in internal initiatives, the study recommends other complementary initiatives in which leaders can participate, such as (for France only) the Climate Businesses Convention or the Impact France Movement, thus strengthening their commitment and the overall impact of the CSR strategy.
In conclusion: initiatives with numerous benefits
The benefits of ecological mobilization initiatives are numerous:
- About the company: these systems transform the practice of the CSR function, allowing it to rely more on employees and be more collaborative. This reduces silo effects, highlights the commitment of "pioneer" employees, and helps to bring out genuinely more sustainable business practices.
- About the collaborators: these systems enhance the collaborators' attachment to the company and address their search for meaning. They strengthen the collaborators' acculturation to ecological issues and legitimize the company's CSR actions. Lastly, they increase the company's attractiveness to committed profiles, who themselves drive transformations.
Our latest articles

Find the ESG reporting software that matches your needs: expert guide + RFP template included
All the best practices for a well-structured RFP process

CSR Strategy: Awareness Programs to Mobilize and Train Teams (ADEME study)
Focus on awareness, with a comprehensive overview of employee mobilization mechanisms in companies.

Benchmark on SaaS Platforms for the CSRD
Explore the key findings from a benchmark by Colombus Consulting and MEDEF, highlighting ESG reporting SaaS platforms, including Greenscope, designed to meet CSRD requirements

The Greenscope guide to the CSRD
Explore how the CSRD transforms corporate transparency and helps your business prepare for compliance and new opportunities



